Intro
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides a numerical representation (scale 0-10) of the severity of an information security vulnerability, it also provides an open framework for communicating the characteristics and severity of software vulnerabilities. CVSS consists of three metric groups: Base, Temporal, and Environmental.
The Base group represents the intrinsic qualities of a vulnerability that are constant over time and across user environments, the Temporal group reflects the characteristics of a vulnerability that change over time, and the Environmental group represents the characteristics of a vulnerability that are unique to a user’s environment.
Base metrics
The Base score is the metric most relied upon by enterprises and deals with the inherent characteristics of a vulnerability, that is, the ones that don’t change over time or due to a user’s environment, such as the degree to which a vulnerability could compromise the confidentiality, integrity or availability (CIA) of the system. It is made up of three sets of metrics.
Exploitability metrics
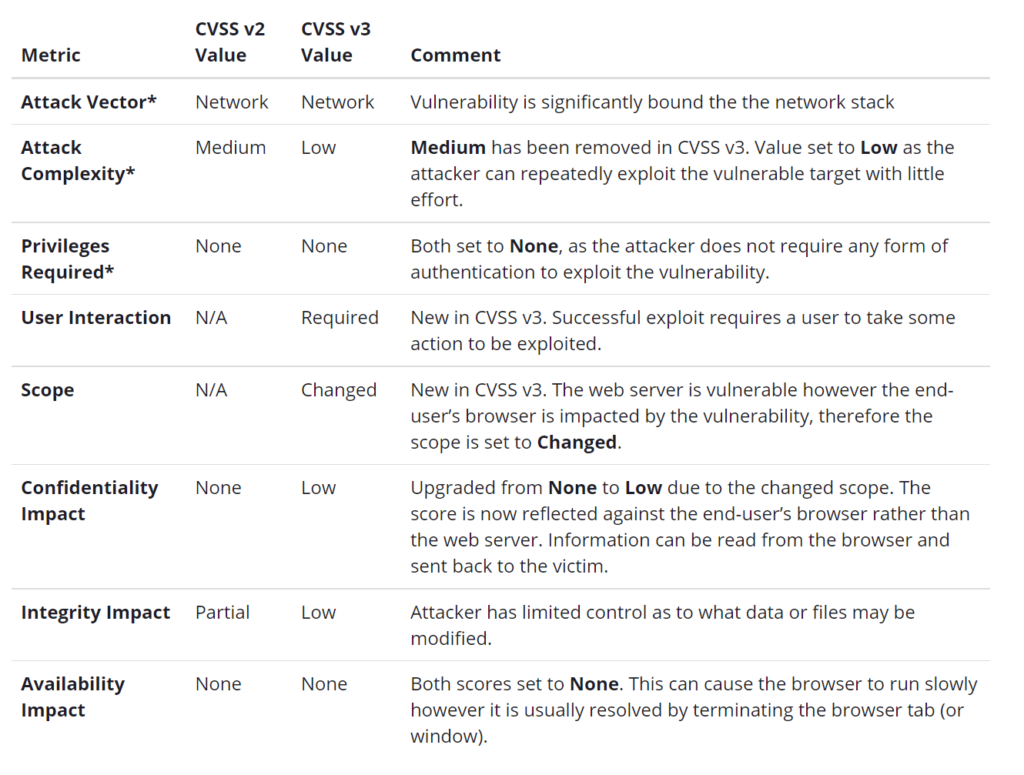
- Attack vector : [Local(L), Adjacent Network(A), Network(N), Physical(P)]
- Attack complexity : [Low(L), High(H)]
- Privileges required : [None(N), Low(L), High(H)]
- User interaction : [None(N), Required(R)]
Impact metrics
- Confidentiality impact : [High(H), Low(L), None(N)]
- Integrity impact : [High(H), Low(L), None(N)]
- Availability impact : [High(H), Low(L), None(N)]
Scope metrics
- Scope : [Unchanged(U), Changed(C)]
Temporal metrics
The Temporal score measures aspects of the vulnerability according to its current status as a known vulnerability, so represents the properties of the vulnerability that do change over time, such as the release of an official patch. It also includes the Report Confidence metric, which measures the degree of confidence in the existence of the vulnerability and the credibility of the known technical details demonstrating that a vulnerability is both real and exploitable. These metrics can decrease or increase the base score, for example if a patch or workaround becomes available, or the vulnerability is validated by the vendor.
- Exploit code maturity : [Not Defined (X), High(H), Functional(F), Proof of Concept(P), Unproven(U)]
- Remediation level : [Not Defined(X), Unavailable(U), Workaround(W), Temporary Fix(T), Official Fix(O)]
- Report confidence : [Not Defined(X), Confirmed(C), Reasonable(R), Unknown(U)]
Environmental metrics
These metrics enable the analyst to customize the CVSS score depending on the importance of the affected IT asset to a user’s organization, measured in terms of complementary/alternative security controls in place, Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. The metrics are the modified equivalent of Base metrics and are assigned values based on the component placement within organizational infrastructure.
Security Requirements (CR, IR, AR).These metrics enable the analyst to customize the CVSS score depending on the importance of the affected IT asset to a user’s organization, measured in terms of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability.
- Security Requirements : [Not Defined(X), High(H), Medium(M), Low(L)]
- Modified Base Metrics : [Modified Attack Vector (MAV), Modified Attack Complexity (MAC), Modified Privileges Required (MPR), Modified User Interaction (MUI), Modified Scope (MS), Modified Scope (MS), Modified Integrity (MI), Modified Availability (MA)] — The same values as the corresponding Base Metric (see above).
Note
CVSS is owned and managed by FIRST.Org, Inc. (FIRST), a US-based non-profit organization.
v3 vs v2
Since it’s first release back in 2005 (v1), CVSS has been widely used in vulnerability management programs for over 15 years. The most recent revision was the move from CVSSv2 to CVSSv3 with CVSSv3.1 being the current revision (released on June 17, 2019). The newer version of CVSS introduces a number of changes in the scoring system that reflect more accurately vulnerabilities that fall under the web application domain, since v2 is still widely adopted/used, it’s worth mentioning the key differences.
New metrics such as Modified Base Metrics, Scope (S) and User Interaction (UI) were added including old metrics such as Authentication (Au) being changed to newer ones such as Privileges Required (PR).
Additional changes occur at the Scoring Scale.
| Scoring Scale | v2 | v3 |
| None | – | 0.0 |
| Low | 0.0 – 3.9 | 0.1 – 3.9 |
| Medium | 4.0 – 6.9 | 4.0 – 6.9 |
| High | 7.0 – 10.0 | 7.0 – 8.9 |
| Critical | – | 9.0 – 10.0 |
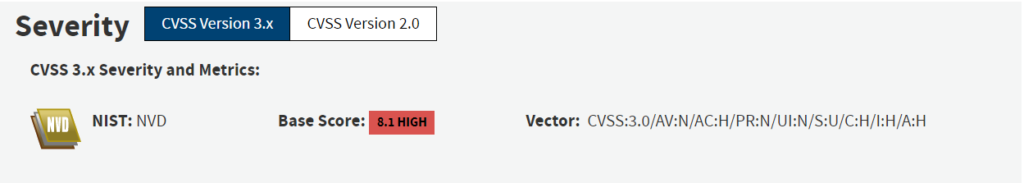


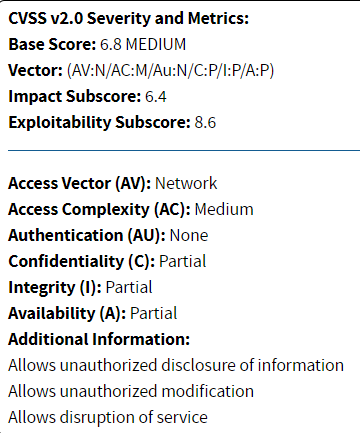
One widely shared criticism of CVSSv3 is that the change in scoring methodology increased the severity of too many vulnerabilities to High or to Critical. In a study conducted by Cisco and Omar Santos, they concluded that the average base score increased from 6.5 in CVSSv2 to 7.4 in CVSSv3. This means that the average vulnerability increased in qualitative severity from “Medium” to “High.” The same study concluded that far more vulnerabilities increased in severity than decreased.
”The CVSS enhancements mean that we will see more vulnerabilities being rated as high or critical throughout the security industry.”
Omar Santos
Although CVSS 3.1 has greatly improved the scoring from version 2, there are still some remaining challenges that will probably be addressed in future releases.
Rabbit Hole
The Evolution of Scoring Security Vulnerabilities
The Evolution of Scoring Security Vulnerabilities: The Sequel